

The maintenance staff who operate the plants every day have little understanding when a process that they have carried out in a certain way for decades in some cases suddenly changes. Accordingly, change management is a key factor for successful implementation. These considerations were taken into account when LSM was developed. For example, it is not mandatory for a company to immediately upgrade to the highest level in every sub-area of maintenance. In a consensus workshop, after diagnosing the current state, a target concept is worked out that specifies which major measures make sense for the company at the moment. This approach is also followed with the Boom Maintenance Manager, which organizes the LSM path in modules. If a company fulfills the prerequisite of a smart criticality assessment, a decision can be made on how to proceed. Besides the maintenance budget planning tool, this is the weakness analysis – both can be combined.
"The essential basic prerequisite for LSM is a clean, process- and digitally-supported maintenance environment. This prerequisite should be met before a company dedicates itself to the topic of LSM."
Christian Zwetti
The Potential Weakness Management (PWM) module enables maintenance managers to perform a comprehensive data-driven weak point analysis and, based on this, plan effective measures to address the weak points. The weakness analysis process follows four simple steps (weakness identification, action derivation, action implementation, effectiveness review) and is supported throughout by the software.
The first step is to determine what should be defined as a vulnerability. “In our experience, many companies see vulnerabilities where the most money needs to be spent. If a process consumes a lot of money, a vulnerability is suspected there. But that doesn’t necessarily have to be the case,” describes Christan Zwetti. Therefore, the criteria for the analysis and the data required for it are defined first. After all, it’s not a matter of recording as much data as possible and then asking yourself the question of how to utilize it – you have to work in a results-oriented manner right from the start. “With this approach, we try to avoid companies falling into the classic stumbling blocks of data analytics.”
The advantages at a glance:
Process analysis attempts to identify patterns that are then applied in predictive maintenance. In this way, one is able to assign specific failures to a set of parameters. For example, if a component exhibits elevated temperature or strong vibrations prior to failure, one can preemptively set a warning value or implement perfective measures to finally eliminate the weak point. In addition to technical vulnerabilities, these can also be organizational problems, which can thus be ruled out in advance.
With the Potential Weakness Management module, the maintenance engineer discovers the causes of malfunctions and understands why a specific fault has occurred. Data-driven weakness analysis makes it possible to prevent malfunctions in advance.
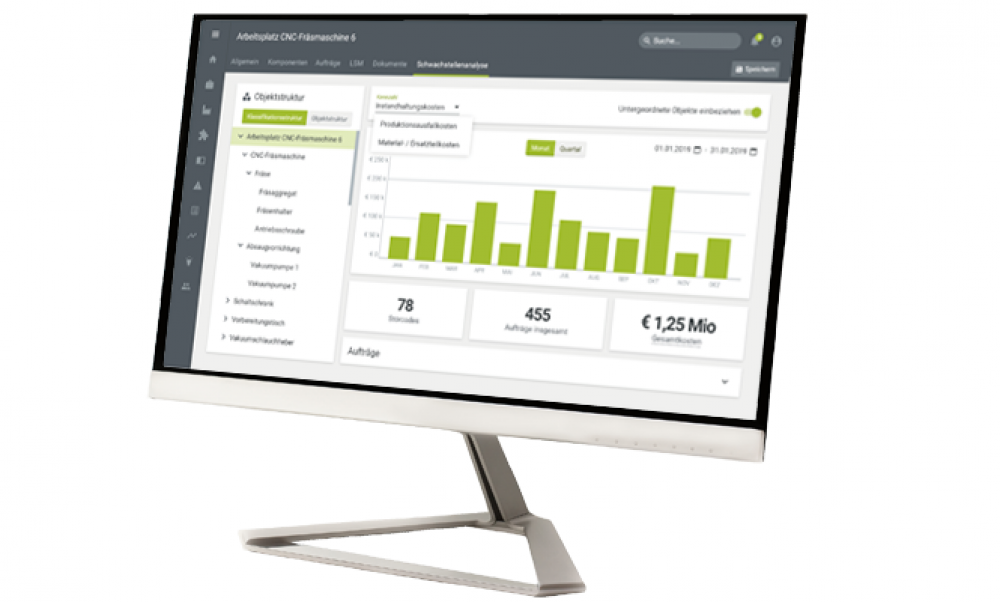
The criticality assessment and the budget planning and weak point analysis modules based on it are the next step of the manufacturing industry in the development towards LSM. The modular design of the Boom Maintenance Manager makes it possible to integrate future developments without any problems. For example, pilot projects are currently underway for Predictive Maintenance or Dynamic Strategy Improvement, which are specifically adapted to the requirements of Industry 4.0.
You want to take the step towards LSM and are looking for a partner who can support you with competence and experience? We have already accompanied several companies on this path. Contact us, we will be pleased to help you!



Receive our latest newsletters directly to your inbox!